Previous Issues Volume 8, Issue 1 - 2024
Determination of the CDR (CDR1, CDR2) Complementary-Determining Region Invertebrate Primitive Antibody from Sea Star
Michel Leclerc*
Immunology of Invertebrates, Orléans University, France
*Corresponding author: Michel Leclerc, Immunology of Invertebrates, Orléans University, France, Tel: 0238410209, Email: [email protected].
Received Date: February 08, 2024
Published Date: February 24, 2024
Citation: Leclerc M. (2024). Determination of the CDR (CDR1, CDR2) Complementary-Determining Region Invertebrate Primitive Antibody from Sea Star. Mathews J Immunol Allergy. 8(1):25.
Copyrights: Leclerc M. © (2024).
ABSTRACT
The IPA (Invertebrate Primitive Antibody) was recently discovered, in the same time of Asterias rubens lymphocytes, humoral specific immune responses and Genomic assays with the sea star IGKappa gene.or anti Horse-radish peroxydase. CDR1 and CDR2 were described in this paper. That corroborates the name of Invertebrate Primitive Antibody and not IG Like protein as it is thought by some people.
Keywords: Invertebrates, Invertebrate Primitive Antibody, CDR1, CDR2.
INTRODUCTION
10 years ago, we tried to clone, for the first time, the Asterias rubens sea star IGKappa gene by the use and the help of E.coli as amplificator [1]. It allowed, in a second time, to verify that the Young Protein, or anti-HRP Protein recognizes the HRP antigen [1].The work which follows was made possible to the great open-mindedness of Dr S.Kossida (IGH Montpellier).
It consists to research Complementary Determining Regions called more briefly CDR1, CDR2, CDR3. Or Complementary-Determining Regions.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
A recalling of the anti -HRP sea star sequence [1] IGKappa gene (Figure 1) and the method of F.Ehrenmann and Lefranc [2,3] from the IMGT V domain directory were used.
First, anti-HRP sequence in nucleotids/
5’GGA TCC GGA GGA ATG CGTGGCAACATGGCGTCTCTATGGATGTTCTTCTT
TGTCGTGGGGATAACTTTACAACGGAGTTTGGCGATTTACACGTTTCGCG
AGCAACCGTCGGACACTAGCGCGTTGCAGGGGAGCACAGTGGTGCTTCAC
TGCTCCGTTGAGCAGTACATAAACACCACGGCCATCGTTTGGTGGAGCCG
TGACTCGGTCATCAGCCACAACAAAGACCTGAAACTGTCCAGTCTAAACA
CCGACCAGCTCCAAAGGTACTCGATTTCAGGCGACGCATCTCGGGGGGAA
TTCAACCTTAAAATAGTGAACTTTACCGCCACAGACGCCGCCAGTTACCG
CTGTCAGATG TAA GAA TTC3’
with the tranlation https://web.expasy.org/translate/
gga tcc gga gga atg cgt ggc aac atg gcg tct cta tgg atg ttc ttc ttt gtc gtg ggg G S G G M R G N M A S L W M F F F V V G ata act tta caa cgg agt ttg gcg att tac acg ttt cgc gag caa ccg tcg gac act agc I T L Q R S L A I Y T F R E Q P S D T S gcg ttg cag ggg agc aca gtg gtg ctt cac tgc tcc gtt gag cag tac ata aac acc acg A L Q G S T V V L H C S V E Q Y I N T T gcc atc gtt tgg tgg agc cgt gac tcg gtc atc agc cac aac aaa gac ctg aaa ctg tcc A I V W W S R D S V I S H N K D L K L S agt cta aac acc gac cag ctc caa agg tac tcg att tca ggc gac gca tct cgg ggg gaa S L N T D Q L Q R Y S I S G D A S R G E ttc aac ctt aaa ata gtg aac ttt acc gcc aca gac gcc gcc agt tac cgc tgt cag atg F N L K I V N F T A T D A A S Y R C Q M taa gaa ttc - E F
Figure 1. Sea star (Starfish) IGKappa gene sequencing.
OR in ANOTHER WAY
MRGNMASLWMFFFVVGITLQRSLAIYTFREQPSDTSALQGSTVVLHCSVEQYINTTAIVWWSRDSVISHNKDLKLSSLNTDQLQRYSISGDASRGEFNLKIVNFTATDAASYRCQMFA
RESULTS
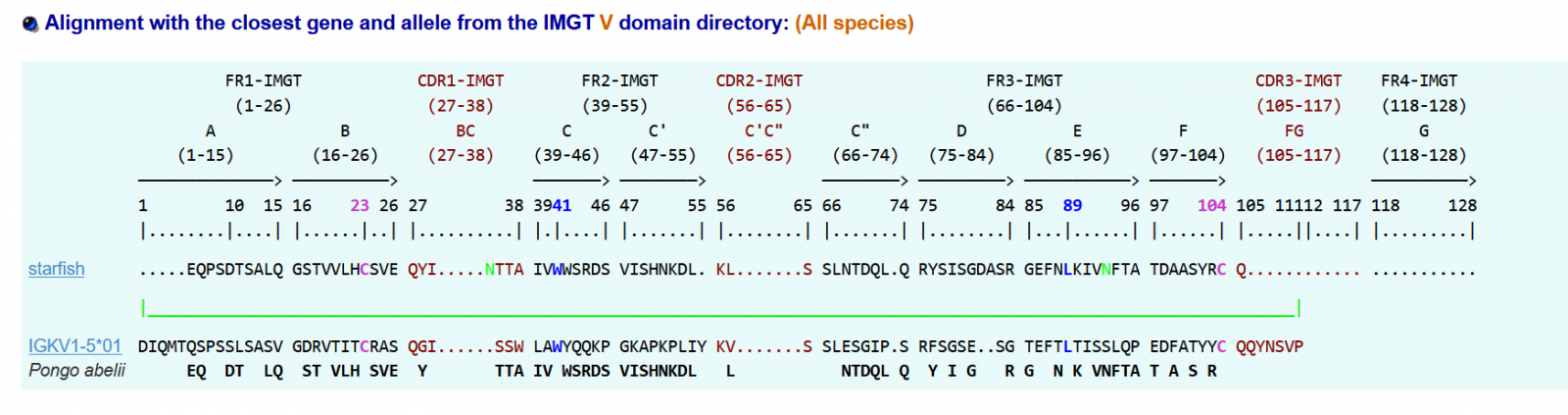
2 tables issued from IMGT resume the following analysis below: I):
https://www.imgt.org/3Dstructure-DB/cgi/DomainGapAlign.cgi with default settings, 17/01/2024
IMGT/DomainGapAlign version: 4.10.3 (2021-12-06)
II) Table II Alignments
>starfish|IGKV1-5*01|33.3|||Pongo abelii
.....EQPSDTSALQGSTVVLHCSVEQYI.....NTTAIVWWSRDSVISHNKDL.KL.......SSLNTDQL.QRYSISGDASRGEFNLKIVNFTATDAASYRCQ.......................
The conserved amino acids (positions 23, 41, 89, 104) are found in the starfish sequence.
This molecule appears to have an IG AA sequence as seen from the above analysis.
1) If it aligns with the Pongo IGKV1-5, the percentage of alignment is 33%, so it is a sequence that seems to have similarities to an IGKV gene when it comes to conserved amino acids.
DISCUSSION
It appears clearly that CDR1 and CDR2 exist in the sea star primitive antibody and not clearly for CDR3 (1 amino acid which is conserved).
Undoubtly
These new parameters [4] corroborate the existence of an Invertebrate Primitive Antbody and NOT IG-LIKE as it is often said. We recall also the discovery by us of T and B sea star lymphocytes [5] Humoral specific response [6] Genomic data [7].
ALL these elements assess the existence of an IPA: Invertebrate Primitive Antibody which shares strong sequence alignments (at least for CDR1 and CDR2) with the Primate: Pongo pygmaeus.
REFERENCES
- Leclerc M, Otten P. (2014). Immune Property Corroborated by A. Rubens Sea Star Igkappa Gene. SAJ Biotechnology. 1:104.
- Ehrenmann F, Kaas Q, Lefranc MP. (2010). IMGT/3Dstructure-DB and IMGT/DomainGapAlign: a database and a tool for immunoglobulins or antibodies, T cell receptors, MHC, IgSF and MhcSF. Nucleic Acids Res. 38(Database issue):D301-D307.
- Ehrenmann F, Lefranc MP. (2011). IMGT/DomainGapAlign: IMGT standardized analysis of amino acid sequences of variable, constant, and groove domains (IG, TR, MH, IgSF, MhSF). Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2011(6):737-749.
- Polonelli L, Pontón J, Elguezabal N, Moragues MD, Casoli C, Pilotti E, et al. (2008) Antibody Complementarity-Determining Regions (CDRs) Can Display Differential Antimicrobial, Antiviral and Antitumor Activities. PLOS ONE. 3(6):e2371.
- Leclerc M, Arneodo VJ, Legac E, Bajelan M, Vaugier GL. (1993). Identification of T-like and B-like lymphocyte subsets in sea star Asterias rubens by monoclonal antibodies to human leucocytes. Thymus. 21(3):133-139.
- Brillouet C, Leclerc M, Binaghi RA, Luquet G. (1984). Specific Immune Response in the Sea Star Asterias rubens: Production of “Antibody-like” Factors. Cell Immunol. 84(1):138-144.
- Vincent N, Osteras M, Otten P, Leclerc M. (2014). A new gene in A. rubens: A sea star Ig kappa gene. Meta Gene. 2:320-322.
.png)